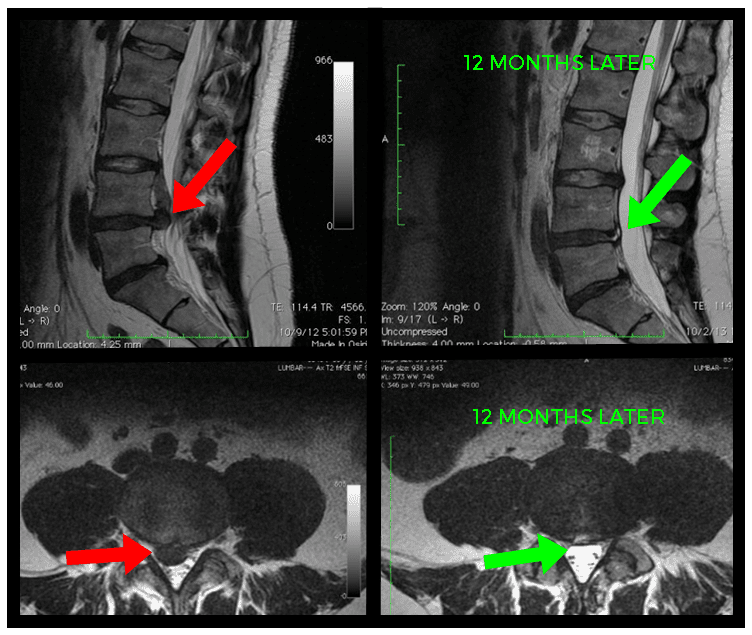
If you’ve been experiencing persistent back pain, tingling sensations, or even weakness in your legs, you might be wondering if a disc protrusion could be the culprit. But can you accurately diagnose this condition just by relying on your symptoms? In this article, we’ll explore the reality of self-diagnosing disc protrusion based on symptoms alone. Grab a cup of tea and get ready to learn more about this common spinal issue and whether you should seek professional medical advice for a proper diagnosis.
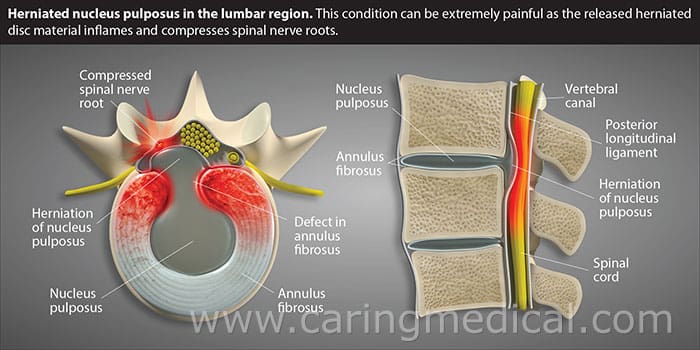
Understanding Disc Protrusion
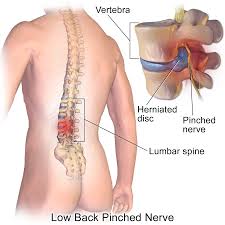
What is Disc Protrusion?
Disc protrusion refers to a condition in which the intervertebral discs, which act as cushions between the vertebrae in the spine, become compressed and bulge outwards. This can occur due to various factors, such as age-related degeneration, spinal injuries, poor posture, or repetitive strain on the spine.
Causes of Disc Protrusion
Disc protrusion can be caused by a multitude of factors, including:
- Age-related degeneration: As we age, the discs in our spine lose their elasticity and water content, making them more prone to bulging.
- Spinal injuries: Trauma or accidents can cause the discs to herniate or protrude.
- Poor posture: Constantly sitting or standing in an improper position for extended periods can place undue stress on the discs, leading to protrusion.
- Repetitive strain: Certain occupations or activities that involve repetitive bending, lifting, or twisting motions can put excessive pressure on the discs and contribute to protrusion.
Symptoms of Disc Protrusion
Disc protrusion can manifest in various symptoms, including:
- Localized or radiating pain: This can occur in the neck, back, or limbs, depending on the location of the protruding disc. The pain may worsen with movement or certain positions.
- Muscle weakness or numbness: The pressure on nerves caused by the protruding disc can lead to weakness or numbness in the affected area.
- Tingling sensation: Nerve compression can also cause a tingling or pins-and-needles sensation, known as paresthesia.
- Loss of range of motion: Disc protrusion can restrict movement and make it difficult to bend, twist, or perform certain activities.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial when it comes to disc protrusion as it helps determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Diagnostic Tools for Disc Protrusion
To accurately diagnose disc protrusion, medical professionals may employ various diagnostic tools, including:
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination allows healthcare providers to assess range of motion, muscle strength, and identify specific pain points.
- Diagnostic imaging: Imaging techniques like X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans can provide detailed visuals of the spine, revealing any abnormalities.
- Specialist consultation: In complex cases or when the symptoms are not clear-cut, a specialist, such as a neurologist, orthopedic surgeon, or physiatrist, may be consulted to provide additional expertise.
Risk of Misdiagnosis
Misdiagnosis of disc protrusion can lead to unnecessary treatments or delays in receiving proper care. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Potential Dangers of Self-Diagnosis
While it may be tempting to rely on self-diagnosis based on internet research or personal experiences, there are inherent dangers involved. Self-diagnosis can lead to misinterpretation of symptoms, incorrect assumptions, and delay in seeking appropriate medical attention.
Common Symptoms of Disc Protrusion
Understanding the common symptoms experienced by individuals with disc protrusion can help identify the condition and guide further medical evaluation.
Localized or Radiating Pain
One of the most prevalent symptoms of disc protrusion is localized or radiating pain. This pain can vary in intensity and may occur in the neck, back, or limbs. The affected area may become tender to touch, and the pain is often exacerbated by movements or certain positions.
Muscle Weakness or Numbness
Disc protrusion can lead to muscle weakness or numbness due to the compression of nerves. These symptoms may occur in the vicinity of the protruding disc or in the limbs depending on the location of the affected disc. Weakness can impede normal functioning, and numbness may result in a loss of sensation.
Tingling Sensation
Nerve compression caused by disc protrusion can result in a tingling or pins-and-needles sensation known as paresthesia. This sensation may be experienced in the area surrounding the protruding disc or radiate to other parts of the body.
Loss of Range of Motion
Disc protrusion can limit the range of motion and flexibility in the affected area. This can make activities like bending, twisting, or lifting difficult and cause discomfort or pain.
Other Conditions with Similar Symptoms
Various conditions can present with similar symptoms to disc protrusion, highlighting the need for accurate diagnosis by a medical professional.
Herniated Disc
Often confused with disc protrusion, a herniated disc occurs when the inner core of the disc protrudes through the outer layer. This can lead to similar symptoms like localized or radiating pain, muscle weakness, numbness, and tingling.
Bulging Disc
A bulging disc refers to a disc that extends beyond its normal boundaries without actually rupturing. While similar to disc protrusion, the symptoms and treatment may vary.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, which may compress the nerves and cause similar symptoms to disc protrusion. It is crucial to differentiate between the two conditions for appropriate treatment.
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease is a condition where the discs lose their cushioning ability and become less flexible. This can result in pain, stiffness, and limited mobility, leading to symptoms that may resemble disc protrusion.
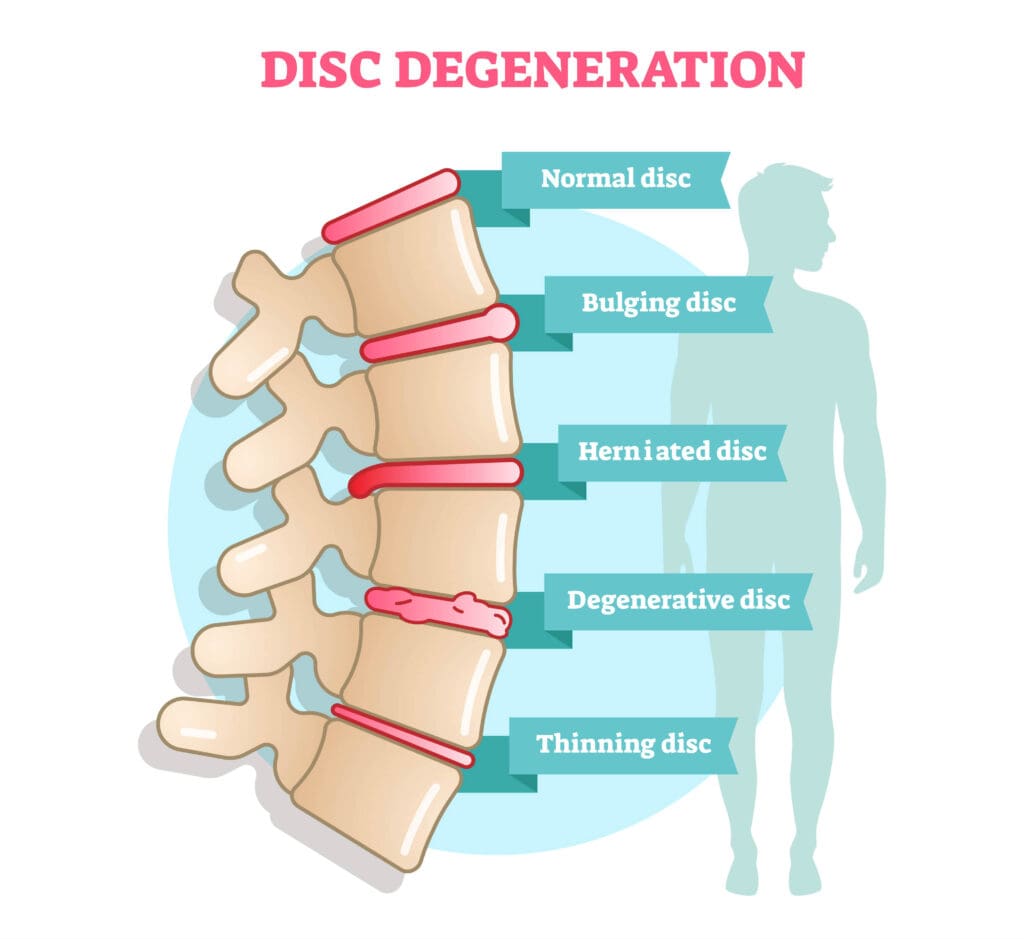
The Role of Medical Professionals
Medical professionals play a vital role in accurately diagnosing and managing disc protrusion. Their expertise and training enable them to conduct comprehensive evaluations and provide appropriate treatment recommendations.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional allows for the assessment of range of motion, muscle strength, and identification of specific pain points. This aids in targeting the affected area and narrowing down potential causes.
Diagnostic Imaging
Imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans provide detailed visuals of the spine, allowing for the identification of abnormalities like disc protrusion. These diagnostic tools can offer valuable insights into the extent of the condition and guide treatment decisions.
Specialist Consultation
In complex cases or when the symptoms are not clear-cut, a specialist consultation may be necessary. Specialists like neurologists, orthopedic surgeons, or physiatrists can provide additional expertise and contribute to the accurate diagnosis and comprehensive treatment plan.
Self-Assessment Tools for Disc Protrusion
In the age of technology, self-assessment tools have emerged to help individuals evaluate their symptoms and potential conditions.
Online Symptom Checkers
Online symptom checkers utilize algorithms to match reported symptoms with possible medical conditions. While these tools can provide general information, they cannot replace the expertise of a medical professional.
Medical Self-Diagnosis Apps
Medical self-diagnosis apps allow users to input and track their symptoms, offering suggestions for potential conditions. However, these apps should be used with caution and not solely relied upon for accurate diagnosis or treatment decisions.
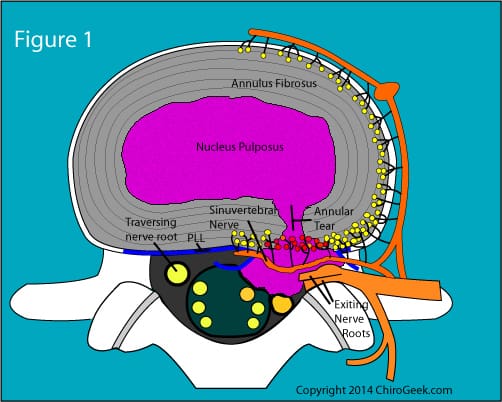
Limitations of Self-Diagnosis
While self-diagnosis tools can provide a starting point, it is essential to recognize their limitations.
Variability in Symptom Presentation
Symptoms of disc protrusion can vary from person to person, and individual experiences may not align perfectly with general descriptions or self-assessment tools. This variability can result in inaccurate self-diagnosis.
Complexity of Diagnosis
Diagnosing disc protrusion involves considering various factors, including medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Self-diagnosis tools often oversimplify the diagnostic process and may overlook important details.
Lack of Physical Assessment
Self-diagnosis relies solely on reported symptoms, without the opportunity for a healthcare professional to conduct a physical examination. Physical assessment is crucial in identifying subtle abnormalities and targeting the appropriate treatment.
When to Seek Professional Medical Opinion
While self-assessment tools can be informative, certain situations warrant seeking professional medical opinion.
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
If symptoms persist or worsen despite self-care measures or if new symptoms emerge, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. Professional medical advice can provide a more accurate evaluation and guide appropriate treatment options.
Emergency Warning Signs
Some symptoms may indicate a medical emergency and require immediate attention. These warning signs include severe pain, loss of bladder or bowel control, sudden weakness or paralysis, or numbness in the groin or rectal area. If any of these symptoms occur, prompt medical intervention is necessary.
The Danger of Delayed Diagnosis
Delayed diagnosis of disc protrusion can lead to significant complications and hinder the effectiveness of treatment.
Complications from Untreated Disc Protrusion
Without timely intervention, disc protrusion can lead to worsening pain, nerve damage, muscle weakness, and impairment in daily activities. Severe cases may require invasive procedures or surgery to alleviate symptoms.
Importance of Timely Treatment
Timely treatment, guided by an accurate diagnosis, is crucial in managing disc protrusion effectively. Early intervention can prevent further damage, improve long-term outcomes, and enhance the overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Seeking professional medical advice is paramount when it comes to accurately diagnosing and managing disc protrusion. While self-assessment tools can provide initial guidance, their limitations and the potential dangers of self-diagnosis should be acknowledged. By working collaboratively with healthcare professionals, individuals can receive the necessary care and make informed decisions regarding their disc protrusion. Additionally, practicing self-care measures, such as maintaining good posture, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress, can empower individuals to take an active role in their overall well-being.